I read something about a new product on Facebook that seems too good to be true, is it?
Short Answer: Probably.
A good general rule in life is if something seems too good to be true it probably is. We get asked everyday about information that is all over Facebook and other media. It is very dangerous to take these at face value, when often they are posted by someone trying to make money. Recently a friend asked about a brand of toothpaste being marketed on Facebook, it was promoted as a new remineralizing agent that would rebuild (heal) the enamel on teeth. They quoted a prominent dental researcher from Japan, who’s research is in remineralization of teeth. He asked me to find out if this toothpaste was legitimate. I went to the companies website, found that they claimed the majority of the research was done by this dentist in her private lab, and a research facility at a university in the UK. I went to the University’s research website and could find no research published on this toothpaste or even this topic in general. I then went to the Research Dentist in Japan’s website. At the top of her website was a Disclaimer, “We are not associated with [toothpaste brand], we do work on products that remineralize teeth, but they are in trial stages and the products we use, if put in the form of a toothpaste, would melt the tissue of your face.”
Our recommendation is that when you see these things, if you feel they might be realistic or beneficial to you, please discuss it with your dentist. Often the home remedies and “Amazing” products online, do not help and are potentially harmful to your teeth and overall health. Your dentist should know about new and upcoming treatments and products. It takes years for some of these new things to pass through health Canada, so by the time they are available everyone knows very quickly because dentists have been waiting for the Health Canada approval to start using it.
In short, Yes those things are probably too good to be true, so please ask a professional.
Can my teeth actually heal themselves?
Short Answer: Yes.
But unfortunately the process by which teeth heal or “remineralize” is much more complex. And it does not happen as easily or quickly as a blog post says it does. Teeth are made up of hydroxyapatite, a complex crystal structure that contains a large amount of calcium. As bacteria consumes the particles of food and sugar left in your mouth, they release acids. These acids eat away Calcium and other minerals weakening the tooth. This is what is known as caries (cavities). If caught very early on, and minerals are available, from diets high in Calcium, Phosphate, Vitamin D or Fluoride, the crystalline structure can rebuild, reduce sensitivity and sometimes even make the tooth stronger. (See “Is fluoride really toxic?”) These small cavities that are caught early on are called incipient caries. You may have seen some the Blogs and facebook posts on How you can heal your teeth, and that your dentist will never tell you that they can. They often use this quote from a well known dental text.
“It has been shown experimentally and clinically that incipient caries [small cavities] of enamel can remineralize.” – Sturdevant’s Art & Science of Operative Dentistry 4th Edition, 2002.
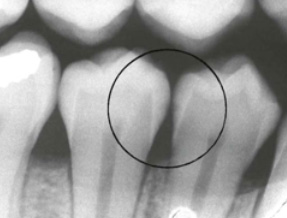
Image A: R1 decay on the premolars
The problem with this is that in the article they avoid explaining what “incipient caries” are. Incipient means “In an initial stage just beginning to happen or develop.” The Picture on the right shows incipient or R1 (Grade 1) decay on the premolars. R1 decay or incipient decay is where the decay is only within the outer surface and the halfway point of the full thickness of the enamel. This decay is often missed, but is the decay that can be repaired if the above steps are taken. Because this decay can range from white to dark black in colour. When healed or Calcified the resultant “arrested caries” (Decay that has stopped progressing), can be a variety of colours and if in an aesthetic area the patient may desire a filling anyways.
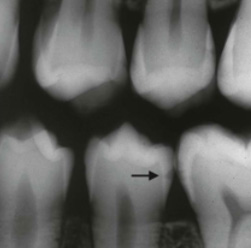
Image B: decay at nearly 100%
It is important to remember that X-rays do not show all of the extent of the decay and decay can be up to 50% LARGER than it actually appears on the x-ray, So when your dentist sees something like image B, where the decay is about at the 100% through the enamel mark. One can be fairly confident that the decays is already through the enamel. Once that enamel barrier is broken. There is no way for you to properly clean inside the tooth and the decay has entered the softer layers of tissue and will progress much more rapidly. A dentist will normally compare your x-rays with the previous ones so that he can see not only where the decay is at, but also how fast it is progressing. If it is progressing slowly, not at all, or is in the incipient stage he may recommend that you alter your oral hygiene habits in order to halt the growth of the decay. However if the decay is progressing over time, and oral hygiene has not helped, or if the decay is large (see Right) the dentist will recommend some form of repair.
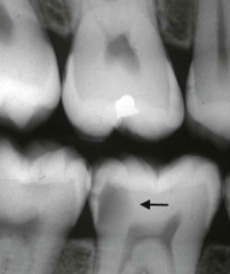
Image C: R4 decay
The Decay in image C is R4 (The decay is beyond halfway between the inner wall of the enamel and the pulp chamber where the blood and nerve supply of the teeth reside. If not dealt with soon this could rapidly progress to very painful decay in the pulp of the tooth or an abscess beneath the root, both of which can only be reversed by a Root Canal Treatment or pulling the tooth.
Is fluoride really toxic?
Short Answer: Yes.
Fluoride is a very potent chemical, That can cause developmental defects, stunt skeletal growth, and was used in World War II by Nazis to make entire populations lethargic, and people put this in our toothpaste and our Water? Yes. With good reason.
Back in 1901 Dr. McKay of the Colorado State Dental Association Set up Practice in Colorado springs and was surprised to find a large portion of the population with Brown stained teeth. Collaborating with Dr. G.V. Black, the Father of Modern Dentistry they discovered that teeth with this brown staining had a very low prevalence of decay. It wasn’t until 1931 that McKay’s years and years of research payed off resulting in the discovery of water borne fluoride.
Fluoride has recently become a large point of controversy, because in high amounts it can be very dangerous. Half a tube of adult toothpaste can be lethal to a 3 year old. However, in low amounts like 0.7 mg/L the fluoride is enough to strengthen the teeth with almost no risk of any other side effects, even the brown stain is not seen at the levels fluoride is used in drinking water. When consumed in amounts that are too high, it can lead to brown stain on teeth and “Colorado Brown Stain” (Fluorosis) Discovered by Dr. McKay.
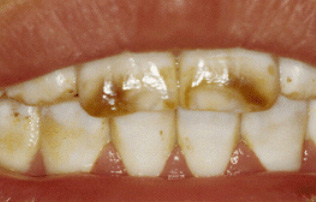 While unsightly, this brown stain is linked with teeth highly resistant to decay. In even higher amounts this may lead to pitting (Large holes on the surface layer of the tooth). However the optimal level shown in the research of lowest risk of side effects and highest effectiveness of the fluoride is 1.1 mg/L in order to be safe, drinking water was lowered to 0.7mg/L.
While unsightly, this brown stain is linked with teeth highly resistant to decay. In even higher amounts this may lead to pitting (Large holes on the surface layer of the tooth). However the optimal level shown in the research of lowest risk of side effects and highest effectiveness of the fluoride is 1.1 mg/L in order to be safe, drinking water was lowered to 0.7mg/L.
Communities like Salmon Arm that have no fluoride in the water need to obtain fluoride from different sources. This can be in the form of a supplement, normal toothpaste, high fluoride toothpastes like Prevident and fluoride treatments from your dentist. Talk to your dentist about what he thinks is best for you in your situation. Fluoride varnishes provide more fluoride and have less risk of swallowing high amounts, these provide more fluoride to your teeth than toothpastes, rinses, and gel trays.
When should fluoride treatment and toothpastes be used?
Water has fluoride at 0.7 mg/L levels. Toothpaste is normally 1-2mg in the .75-1.25ml commonly used when brushing. Toothpaste is normally about 1500 ppm fluoride.
Keep toothpaste out of reach of small children! Always remember half a tube of 1500ppm toothpaste could be lethal to a 3 year old.
- Age 0-2: Fluoride toothpastes are not recommended, if in a fluoridated area the child should get enough from the water, if not, and your child is high risk of decay, your dentist may recommend it though.
- Age 3-6: Normally at this age you should use non-fluoridated toothpaste. Why? Your child cannot spit out the toothpaste. They may be able to spit, but not the entire amount that they put in, which means they are swallowing a lot of toothpaste. If you’re water is not fluoridated talk with your dentist. He may recommend using a “RICE-SIZED” amount (not pea sized) of fluoridated toothpaste once every week or two. Do not start using fluoridated toothpaste without talking to a dentist. Your child should get fluoride varnish every 6 mo or 12mo, at the dentist.
- Age 6-8: Start with Rice-sized amounts of fluoridated toothpaste. Do a spit test to see if your child can spit out their toothpaste before starting regular use of fluoridated toothpaste. Regular fluoride varnish applications at the dentist are recommended.
- Age 8-12: Pea sized amounts of Fluoride toothpaste, along with regular fluoride varnish done at the dentists.
- Age 12-18: Children should be able to regulate their own toothpaste use at this point. Larger amounts for a larger child, although even an adult does not need enough to cover the entire toothbrush. Still doing fluoride varnish applications is recommended at the dentists.
- Age 18+: It is no longer recommended to apply Fluoride varnish yearly at the dental office unless in a high-risk for decay situation. Lots of decay each year, nonfluoridated water community, or difficulty in brushing. Older patients, or disabled patients, may require help in brushing and flossing and may again need fluoride varnishes to aid the prevention of weakening their teeth. Ask your dentist if you are high risk and need fluoride supplementation or varnish treatment.
Are my fillings causing mercury poisoning?
Do my fillings contain mercury?: Yes.
Is that Mercury Toxic: No.
Can you react to it: There is a very rare possibility of reaction to Amalgam (mercury) fillings. Amalgam (Mercury) Fillings are still considered a standard in Dentistry. They are the best material when the situation does not allow a dry surface to bond the Composite (White) Fillings to. The amalgam is also slightly better at standing up to the strong biting forces on the molars. (Part of the reason your insurance company will only pay the fee of the “silver fillings” if you get a white filling on your molars.)
So what about the mercury in these fillings? Mercury is found in the filings as are many other metals, copper, zinc, nickel, and others depending on how old the Amalgam is it may contain different metals. The Mercury used is Elemental Mercury, which is pure, and not Organic Mercury which can break the Blood-Brain Barrier, and be absorbed through the stomach, leading to Mercury Poisoning etc. Elemental Mercury is not absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract. Also the mercury is mixed and by the time you leave the chair it is hard enough that little to no mercury is going to leach out of the filing as it has bonded into an alloy with the other metals present.
Should you remove them all? If your concern is the mercury, then No. You are actually exposing yourself to more mercury by removing them than you would by having them in your moth the rest of your life. Also, replacing a filling means losing more tooth structure. If your concern is aesthetic then yes, or if the fillings are very old and starting to get decay under them then of course.
All that being said, in rare cases people do react to their Amalgam fillings although usually these people also react to cheap jewelry and items with nickel and sometimes other metals. If you do have an allergy to some base metals it would be a good idea to discuss this with your dentist.
Why do we take out our wisdom teeth?
There are a number of reasons:
- Teeth are decayed and you are unable to brush them.
- They are partially impacted and at high risk of becoming infected.
- They are fully impacted but may become an issue in the future, and you are currently insured but may not be insured in the future, although there are options such as uprighting your wisdom teeth, see below.
- They hurt or are already abscessed.
According to some Facebook articles, Wisdom teeth are key to the health of your liver because the nerves in your teeth are linked to other areas of your body. Clearly all your nerves are connected through your brain, but removing this tooth will not damage your liver. The article is right that there are risks of Paresthesia (temporary or permanent feeling loss) after the extraction, however this is a risk, albeit less of one, in all extractions and oral injections. This usually only lasts for a couple of weeks to a couple of months. This article would also have you believe that wisdom teeth are removed because our hygienists are lazy, and don’t want to clean them. We always want you to keep all your teeth if this is a possibility, and if we all had the room for our wisdom teeth to come in and not cause issues we would see a lot less of them extracted.
There are treatments available that can reduce the risks of these extractions by uprighting and allowing the wisdom teeth to erupt fully into the oral cavity. By erupting the wisdom teeth we may allow them to either be kept or be removed by less invasive methods. Talk to your dentist to find out if the option of uprighting your wisdom teeth is for you. What do you have to loose, besides the teeth that you were going to loose anyways.
Is it healthier to use a natural toothpaste or the stuff from the store?
You’ve probably seen a million different Facebook recipes for toothpaste. Ranging from straight peroxide to Lemon juice and baking soda. The thing to remember is what causes decay. Toothpaste has been through rigorous research and study to find formulas that will reduce the chance of decay. The fluoride in them is essential especially if you live in an area with nonfluoridated water. Chemicals like peroxide that dry out your mouth or Lemon juice that is a strong enough acid to eat the enamel in your teeth, create a dry acidic environment that the bacteria that cause decay will thrive in. It is important to use things that do not dry out your mouth, and reduce the acids in your mouth, in order to prevent decay.
Insurance Coverage/Payment
It is your responsibility to know your insurance’s coverage and plan maximum and fee guide. As a courtesy to our patients we do electronic billing to your insurance on your behalf. We will do pre-authorizations on major dental treatment, however, due to the privacy act it is your responsibility to follow up with the insurance and inform us. Please be aware that if for any reason the claim is rejected or not paid in full, you are financially responsible for the balance on date of service.
It is customary that payment is due as services rendered. We accept cash, interact, MasterCard, Visa, and personal cheques.
More information on Dental Financing can be found at: https://www.dentalcard.ca
Are x-rays safe?
This is a field that has changed a lot in the last decade. The amount of radiation needed to take standard dental x-rays has gone way down, the film technology is continuing to change allowing us to significantly reduce exposure time. During our lives we are continually picking up background radiation from the earth and the atmosphere around us. We calculate the amount of radiation that an x-ray uses in BERTs (Background Equivalent Radiation Time) in units of days adn hours. The standard 2 bitewing xrays that you have at your yearly check-up, are the equivalent to the amount of radiation you pick up in 14 hours. If your dentist is using digital x-rays your exposure is even less.
Another way of calculating radiation is in BED units (Banana Equivalent Dose) Bananas contain natural radiation because of the isotopes that they contain. Dental X-rays are somewhere around 50 BED. Close to eating about 50 bananas. Contrast that with the natural radiation from potassium isotopes in your body over a year which is about 3900 BED, or a flight from New York to LA which is around 400 BED. Basically you could have 8 sets of x-rays.
If x-rays are so safe, why do I wear a lead apron, and why does the assistant run out of the room?
Recent studies have showed that the amount of radiation from Dental X-rays are so low that the apron is really not necessary any more, unless the patient is pregnant. However, we don’t know how much radiation you receive on a regular basis. You may live in an area with higher background radiation, you may have had a full body CT scan last week, or you may be receiving radiation treatment for something else, and so limiting the amount of radiation is always the best practice. In most instances rather than explaining that there is not a need for the apron, or determining the level of need for protection it is less time consuming and just makes more sense to protect everyone. We leave the room because we are exposed many times a day, and lowering the level of radiation that you are exposed to is always the best practice, your dentist will only ask for x-rays if he feels it is necessary and the benefit outweighs any risk.
What do I need to know about dentures if i’m getting new ones or have had them for a long time?
What are Dentures?
Many people around you wear dentures, and most of the time you would never know. They are artificial teeth that can be easily removed and replaced by the wearer. They are the most cost effective way to replace your missing teeth.
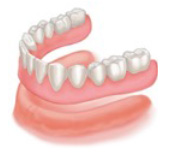
Complete lower denture
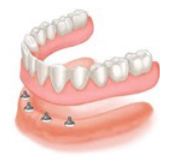
Complete lower implant supported denture
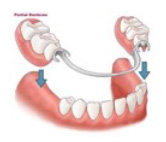
Partial lower denture
Will I notice them?
Dentures can take 2-6 months to get used to. You are probably used to limited chewing surface or no teeth at all, and having new dentures your mouth will feel abnormally full. You will sound funny when you talk, eating and drinking will be foreign. Eventually you will get used to them. The fit of them may change over the years and you may need to have them relined (adjustment of the surface that contours to create a better fit). Keep in mind as well if you opted for the immediate dentures (teeth out and denture in same day), for the first month your dentures are more of a bandaid, and an aesthetic accessory than a functional denture. Once healing has occurred make sure you come in for your soft relines.
Here are some things that will help you get used to wearing your dentures:
- Drink lots of water
- Massage your gums
- Use adhesives for better fit, usually where the anatomy of the bone structure is not conducive to a stable denture base.
Eating
You may bite your cheek and tongue for the first while with new dentures. Chewing tough or fibrous foods such as steak or lettuce, may be difficult to chew. Chewing slowly and avoiding tough foods is a good idea. Steaming your vegetables will help also.
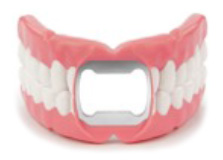
Your Dentures are more fragile than your natural teeth. Opening bottles, cracking nuts, etc. will damage your dentures.
Speaking
Reading out loud to yourself or videotaping yourself speaking, will help you figure out how your dentures work into your scheme of speech. You can ask someone to listen to you to help you hear the differences that subtle changes in your functioning make. But keep in mind you will most likely notice the change in your speech more than anyone else.
Cleaning
Wear your glasses/contacts while cleaning so you can see the areas that need to be cleaned.
Fill the sink with a towel or water so that if you drop the denture the porcelain does not cause anything to be broken.
Brush your denture. It is not necessary and can even be harmful to the denture to use toothpaste. Toothpaste is very abrasive. Don’t hold your denture by the back teeth on both sides at the same time as this pinching motion will break the denture. Always hold the denture by one side.
Brush your gums and existing teeth. It is very important to maintain the health of the gums and save any teeth that are left.
 Clean your dentures every day and rinse them with water after every meal.
Clean your dentures every day and rinse them with water after every meal.
Soak your denture overnight in water or denture cleaner. It will help kill bacteria that live in the acrylic, and it is good to give your tissues a rest. Check any cleaner you use to make sure that it is safe for your denture. Some cleaners may damage metal dentures. If your dentures are out of the mouth make sure that they are soaking in water, so that they don’t dry out.
 Some recent research points to a link between sleeping without your dentures and sleep apnea. This is because the airway collapses without the dentures to hold it in it’s natural position. If you find sleeping without your dentures causes you to have restless and/or uncomfortable sleep or you are tired all the time, fall asleep anywhere even sometimes while driving. You may struggle with sleep apnea and it would be a good idea to sleep with you dentures in, but make sure you find some other time during the day to give your tissues a break for at least 3-4 hours a day.
Some recent research points to a link between sleeping without your dentures and sleep apnea. This is because the airway collapses without the dentures to hold it in it’s natural position. If you find sleeping without your dentures causes you to have restless and/or uncomfortable sleep or you are tired all the time, fall asleep anywhere even sometimes while driving. You may struggle with sleep apnea and it would be a good idea to sleep with you dentures in, but make sure you find some other time during the day to give your tissues a break for at least 3-4 hours a day.
